Low Carb High Protein Diet for Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide (LCHP)
Authored by Mansi Bhatt
What is the Low-Carb High-Protein (LCHP) Diet?
The low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes is more than just a popular trend. It is a structured approach that emphasizes cutting down carbohydrates while increasing protein intake. By reducing carbs, blood sugar fluctuations are minimized, and by increasing protein, the body benefits from improved satiety and muscle preservation. This makes it one of the best diets for type 2 diabetes when followed under professional guidance.
Unlike generic calorie restriction, the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes balances carbs, protein, and healthy fats in a way that directly addresses insulin resistance. To pair nutrition with outcomes like fat-loss and medication reduction, explore our integrated care at Diabetes Reversal and Obesity Reversal.
How the LCHP Diet Helps in Type 2 Diabetes Management
Managing type 2 diabetes is not only about avoiding sugar — it is about balancing the right nutrients. The LCHP diet brings together low-carb principles and protein-and-healthy-fat–focused meals to target the root cause of blood sugar instability. Here’s how it works in practice:
Controlling Blood Sugar with Fewer Carbs
A low carb diet for diabetes reduces glucose surges after meals. With fewer carbs, there is less demand for insulin, resulting in steadier blood sugar and improved HbA1c.
Protein’s Role in Satiety and Muscle Preservation
Protein is the backbone of a high protein diet for diabetes. It reduces hunger, supports muscle mass, and helps patients avoid overeating — a common struggle in insulin resistance.
Impact on Insulin Resistance and Weight Loss
An insulin resistance diet plan enhances the body’s ability to respond to insulin. With balanced protein and healthy fats, weight loss becomes easier, and fat metabolism improves, reducing long-term diabetes risks. Nutrition changes often complement blood pressure improvements as well—see Hypertension Reversal.
Benefits of the Low-Carb High-Protein Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
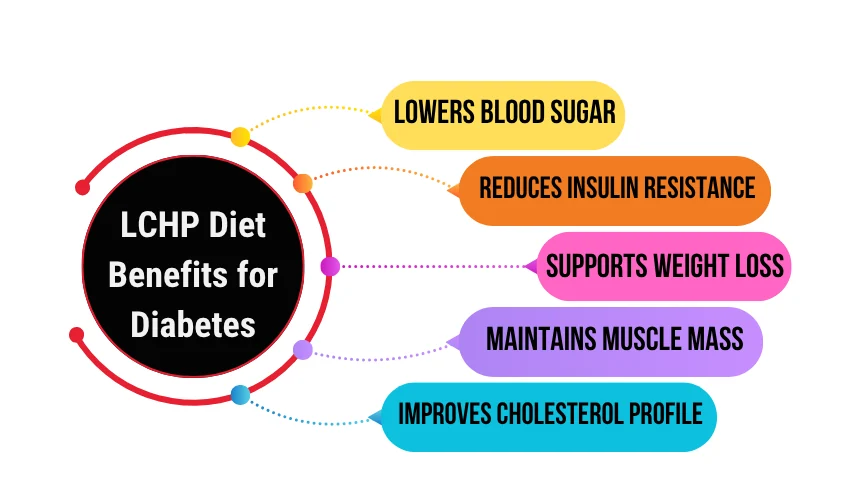
- Stabilizes fasting and post-meal blood sugar.
- Promotes fat loss while preserving muscle.
- Improves insulin sensitivity.
- Reduces cravings and emotional eating.
- Works as a diet to lower blood sugar naturally.
Risks and Considerations of the LCHP Diet
No diet is one-size-fits-all, and the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes requires proper monitoring. Before starting, patients should be aware of a few considerations:
- Those with kidney issues may need moderated protein.
- Carb reduction can initially cause fatigue.
- Medication doses may need adjustment with improved sugar control.
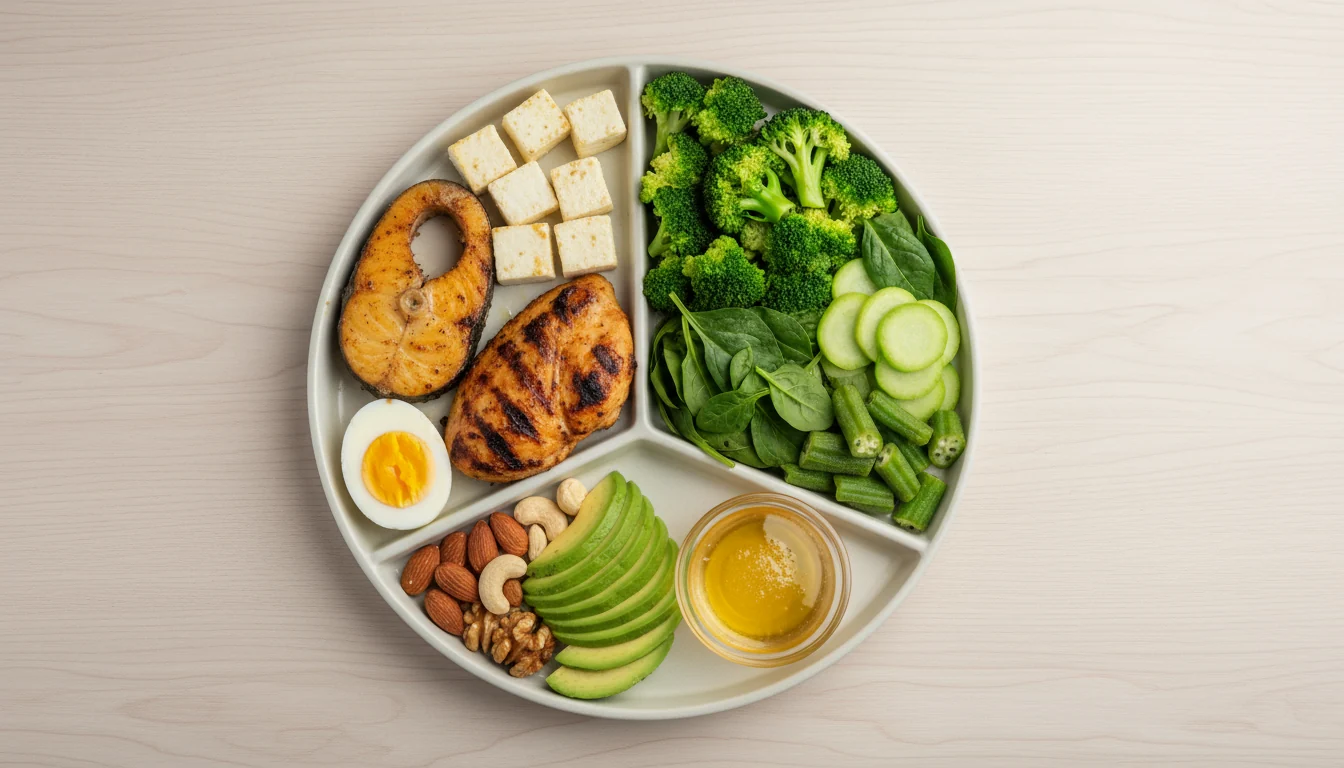
Foods to Eat on a Low-Carb High-Protein Diet
Choosing the right foods is the heart of an effective insulin resistance diet plan. The goal is to maximize nutrient-dense proteins and low-glycemic vegetables.
- Proteins: Eggs, mutton, chicken, fish, paneer, tofu, tempeh, soya chunks.
- Healthy fats: Desi ghee, white makkhan, extra virgin olive oil, virgin coconut oil.
- Non-starchy vegetables: Lauki, bhindi, cucumber, cauliflower, cabbage, turai.
- Low-GI fruits: Berries, avocado, kiwi.
Foods to Avoid in a Low-Carb High-Protein Diet
Knowing what not to eat is as important as what to eat. Avoiding sugar-spiking foods ensures better control. Below are the key foods to avoid with type 2 diabetes:
- Refined carbs (white rice, bread, biscuits).
- High-sugar fruits (mangoes, bananas, grapes).
- Processed snacks (muesli, “protein” bars, packaged juices).
- High-carb grains (corn, wheat).
Sample Low-Carb High-Protein Meal Plan for Type 2 Diabetes
Meal planning brings theory into practice. Here’s an example of a simple, effective low carb diet for diabetes that balances protein, healthy fats, and low-GI veggies.
- Breakfast: Paneer bhurji / egg bhurji with palak in desi ghee
- Lunch: Grilled chicken / grilled tofu + cucumber salad + lauki sabzi
- Dinner: Fish tikka / tempeh tikka + cauliflower mash + bhindi sabzi
Lifestyle Tips to Maximize LCHP Diet Benefits
A diet works best when combined with healthy lifestyle choices. Along with the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes, patients should also focus on:
- 30 minutes of strength training.
- Staying hydrated throughout the day.
- Prioritizing good sleep to reduce insulin resistance.
- Eating 2–3 filling meals instead of constant snacking.
Redial Clinic’s Approach to the LCHP Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
At Redial Clinic, Green Park, Delhi, we go beyond generic plans. We create individualized insulin resistance diet plans that suit your lifestyle, medical reports, and preferences. By using real, local foods, the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes becomes a sustainable pathway to long-term sugar control and reversal. Start here: Diabetes Reversal · Obesity Reversal · Hypertension Reversal.
Final Verdict
The evidence strongly supports the role of the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes in improving sugar control, reversing insulin resistance, and helping with weight loss. Patients adopting this plan experience more energy, fewer sugar crashes, and long-term health improvements.
At Redial Clinic, we help patients move away from sugar-spiking meals toward sustainable, protein-rich foods. With the right insulin resistance diet plan, reversing diabetes becomes a real possibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is the low-carb high-protein diet safe for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, when supervised by healthcare professionals, the low carb high protein diet is both safe and effective.
Can the LCHP diet help reverse diabetes naturally?
Yes, it works as a diet to lower blood sugar naturally by reducing carb intake and improving insulin sensitivity.
What are the best high-protein foods for type 2 diabetics?
Eggs, paneer, chicken, fish, tofu, tempeh, and Greek yogurt are the core of a high protein diet for diabetes.
Can vegetarians follow a low-carb high-protein diet for diabetes?
Yes. Paneer, tofu, tempeh, soya chunks, and Greek yogurt make the low carb high protein diet for type 2 diabetes vegetarian-friendly.
References
| No. | Reference | Key Finding |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes — 2024. Diabetes Care. | Recommends low-carb approaches as effective for lowering HbA1c. |
| 2 | Feinman RD, et al. Dietary carbohydrate restriction as the first approach in diabetes management. Nutrition. 2015. | Demonstrates improved glycemic control with carb restriction. |
| 3 | Mansoor N, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets on weight and glycemic control. Nutrition Reviews. 2016. | Shows weight loss and blood sugar benefits of LCHP diets. |
| 4 | Gannon MC, Nuttall FQ. Effect of a high-protein, low-carb diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004. | Found improved glucose response with higher protein intake. |
| 5 | Tay J, et al. Comparison of low-carbohydrate and high-carb diets in type 2 diabetes. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2015. | LCHP diet improved HbA1c, weight, and insulin sensitivity. |






