Bananas and Diabetes: Can You Eat This Sweet Fruit Without Worry?
When it comes to bananas and diabetes, confusion is common. Bananas are affordable, convenient, and widely promoted as a healthy snack. But are they suitable for someone working on diabetes control or reversal?
The truth is that despite containing potassium and vitamin B6, bananas carry a high sugar and carbohydrate load. The bananas glycemic index falls in the medium-to-high range, which means they can spike blood sugar quickly. At Redial Clinic, Delhi, our stance is straightforward—bananas and diabetes don’t mix if your goal is true reversal.
The Relationship Between Bananas and Diabetes
Many assume bananas are harmless, but for diabetics they can cause unwanted glucose spikes. Understanding how bananas affect glucose levels is crucial for smart dietary decisions.
Nutritional Profile of Bananas
A medium banana (~118 g) provides:
- Carbs: 27 g
- Sugar: 14 g
- Fiber: 3 g
- Protein: 1.3 g
- Potassium: 422 mg
While nutritious, the carb load makes the bananas and diabetes combination risky.
How Bananas Affect Glucose Levels
Bananas break down rapidly into glucose, spiking blood sugar. Studies confirm ripe bananas behave almost like sugar water for diabetics. This is why we tell patients that bananas and diabetes simply don’t align when the goal is reversal.
Bananas in a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
Some people believe eating only half a banana or pairing it with nuts makes it safe. But clinical results say otherwise—even small portions can elevate sugar significantly.
At Redial Clinic, we don’t recommend bananas in a structured diabetes reversal plan.
Bananas’ Glycemic Index & Glycemic Load
Bananas fall into a medium GI category, creating significant glucose spikes.
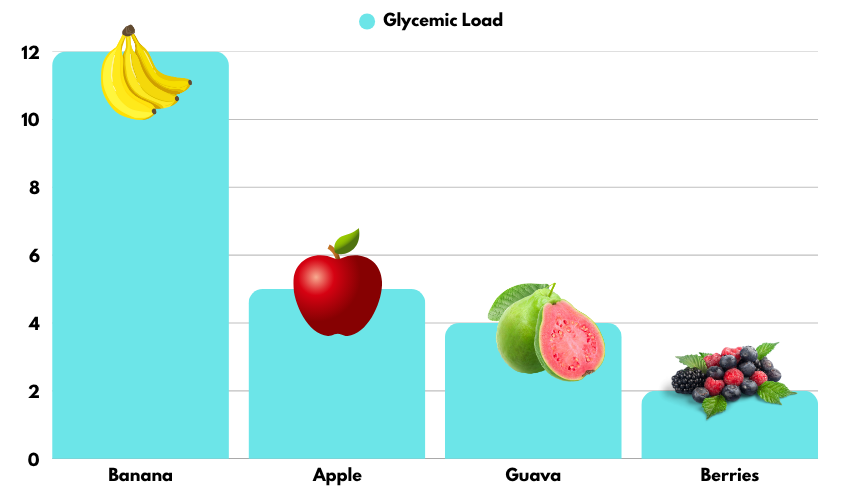
| Ripe Banana | GI ~62 | GL ~16–17 |
| Unripe Banana | GI ~42–48 | GL ~11–12 |
| Apple | GI ~36 | GL ~5 |
| Berries | GI 25–40 | GL ~2 |
| Guava | GI ~24 | GL ~4 |
This clearly shows why bananas and diabetes are not a safe pairing.
Unripe vs Ripe Bananas: Which is Better?
Unripe bananas contain more resistant starch, but they still raise sugar enough to be discouraged. In the unripe vs ripe banana debate, neither is suitable for diabetics.
Health Benefits of Bananas — But at What Cost?
Yes, bananas offer potassium and B6. However, diabetics can get these nutrients from safer foods.
Examples:
- Leafy greens (magnesium, potassium)
- Chia & pumpkin seeds (fiber, minerals)
- Avocado (healthy fats, low carbs)
Best Alternatives to Bananas for Diabetics
Swap bananas for:
- Guava
- Berries
- Kiwi
- Avocado
These fruits fit well in a diabetes & obesity reversal plan.
How Redial Clinic Helps Patients Make Smart Food Choices
We use CGM data to teach patients how foods like bananas trigger glucose spikes. Instead, we recommend low-GI fruits and a metabolic wellness plan personalized for Indian eating habits.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: bananas and diabetes are not a good match. Their glycemic index and sugar density destabilize glucose, making diabetes reversal harder.
FAQs
Can diabetics eat bananas?
Not recommended. Even small portions spike sugars.
Are unripe bananas safe?
Slightly better but still not ideal for reversal.
Best diabetic-friendly fruits?
Guava, berries, kiwi, avocado.
Final Verdict
For diabetes control or reversal, avoid bananas. Choose lower-GI fruits and follow a monitored nutrition strategy.
References
| 1 | American Diabetes Association | Bananas should be limited due to GL impact. |
| 2 | Harvard GI Chart | Bananas medium-high GI; better replacements exist. |
| 3 | ADA Journal 2021 | Low-GI fruits improve HbA1c. |






